Deepdream in TensorFlow
Contents
# Install the necessary dependencies
import os
import sys
!{sys.executable} -m pip install --quiet pandas scikit-learn numpy matplotlib jupyterlab_myst ipython imageio scikit-image requests pillow
23.10. Deepdream in TensorFlow#
Note: There is no new code in this script. It originates from the TensorFlow tutorial located here. However, this code is modified slightly to run on Python 3. The code is also commented very heavily to explain, line-by-line, what occurs in the deepdream demo.
Here are some potential outputs.
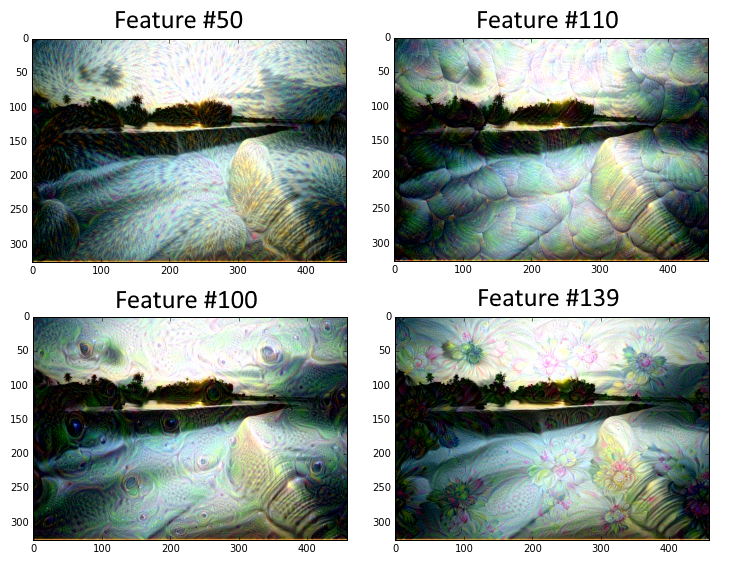
Fig. 23.4 name: Deepdream outputs#
23.10.1. Code#
Using TensorFlow for Deep Dream
From: Alexander Mordvintsev https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/deepdream
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import IPython.display as display
import PIL.Image
url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg'
# Download an image and read it into a NumPy array.
def download(url, max_dim=None):
name = url.split('/')[-1]
image_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file(name, origin=url)
img = PIL.Image.open(image_path)
if max_dim:
img.thumbnail((max_dim, max_dim))
return np.array(img)
# Normalize an image
def deprocess(img):
img = 255*(img + 1.0)/2.0
return tf.cast(img, tf.uint8)
# Display an image
def show(img):
display.display(PIL.Image.fromarray(np.array(img)))
# Downsizing the image makes it easier to work with.
original_img = download(url, max_dim=500)
show(original_img)
display.display(display.HTML('Image cc-by: <a "href=https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Felis_catus-cat_on_snow.jpg">Von.grzanka</a>'))
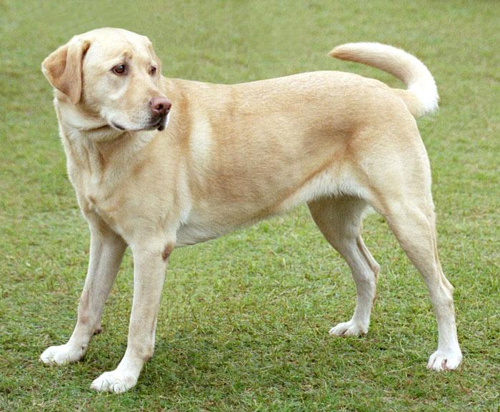

Image cc-by: Von.grzanka
base_model = tf.keras.applications.InceptionV3(include_top=False, weights='imagenet')
# Maximize the activations of these layers
names = ['mixed3', 'mixed5']
layers = [base_model.get_layer(name).output for name in names]
# Create the feature extraction model
dream_model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=layers)
def calc_loss(img, model):
# Pass forward the image through the model to retrieve the activations.
# Converts the image into a batch of size 1.
img_batch = tf.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
layer_activations = model(img_batch)
if len(layer_activations) == 1:
layer_activations = [layer_activations]
losses = []
for act in layer_activations:
loss = tf.math.reduce_mean(act)
losses.append(loss)
return tf.reduce_sum(losses)
class DeepDream(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
self.model = model
@tf.function(
input_signature=(
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[None,None,3], dtype=tf.float32),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[], dtype=tf.int32),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[], dtype=tf.float32),)
)
def __call__(self, img, steps, step_size):
print("Tracing")
loss = tf.constant(0.0)
for n in tf.range(steps):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# This needs gradients relative to `img`
# `GradientTape` only watches `tf.Variable`s by default
tape.watch(img)
loss = calc_loss(img, self.model)
# Calculate the gradient of the loss with respect to the pixels of the input image.
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, img)
# Normalize the gradients.
gradients /= tf.math.reduce_std(gradients) + 1e-8
# In gradient ascent, the "loss" is maximized so that the input image increasingly "excites" the layers.
# You can update the image by directly adding the gradients (because they're the same shape!)
img = img + gradients*step_size
img = tf.clip_by_value(img, -1, 1)
return loss, img
deepdream = DeepDream(dream_model)
def run_deep_dream_simple(img, steps=100, step_size=0.01):
# Convert from uint8 to the range expected by the model.
img = tf.keras.applications.inception_v3.preprocess_input(img)
img = tf.convert_to_tensor(img)
step_size = tf.convert_to_tensor(step_size)
steps_remaining = steps
step = 0
while steps_remaining:
if steps_remaining>100:
run_steps = tf.constant(100)
else:
run_steps = tf.constant(steps_remaining)
steps_remaining -= run_steps
step += run_steps
loss, img = deepdream(img, run_steps, tf.constant(step_size))
display.clear_output(wait=True)
show(deprocess(img))
print ("Step {}, loss {}".format(step, loss))
result = deprocess(img)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
show(result)
return result
dream_img = run_deep_dream_simple(img=original_img,
steps=100, step_size=0.01)
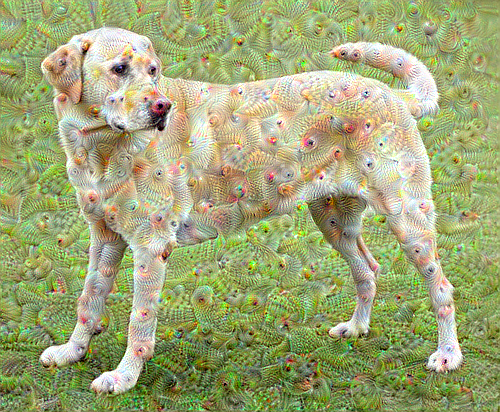

import time
start = time.time()
OCTAVE_SCALE = 1.30
img = tf.constant(np.array(original_img))
base_shape = tf.shape(img)[:-1]
float_base_shape = tf.cast(base_shape, tf.float32)
for n in range(-2, 3):
new_shape = tf.cast(float_base_shape*(OCTAVE_SCALE**n), tf.int32)
img = tf.image.resize(img, new_shape).numpy()
img = run_deep_dream_simple(img=img, steps=50, step_size=0.01)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
img = tf.image.resize(img, base_shape)
img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img/255.0, dtype=tf.uint8)
show(img)
end = time.time()
end-start

6.457822322845459
23.10.2. Your turn! 🚀#
You can practice your cnn skills by following the assignment sign language digits classification with cnn
23.10.3. Acknowledgments#
Thanks to TensorFlow for creating the open source project DeepDream. It inspires the majority of the content in this chapter.


